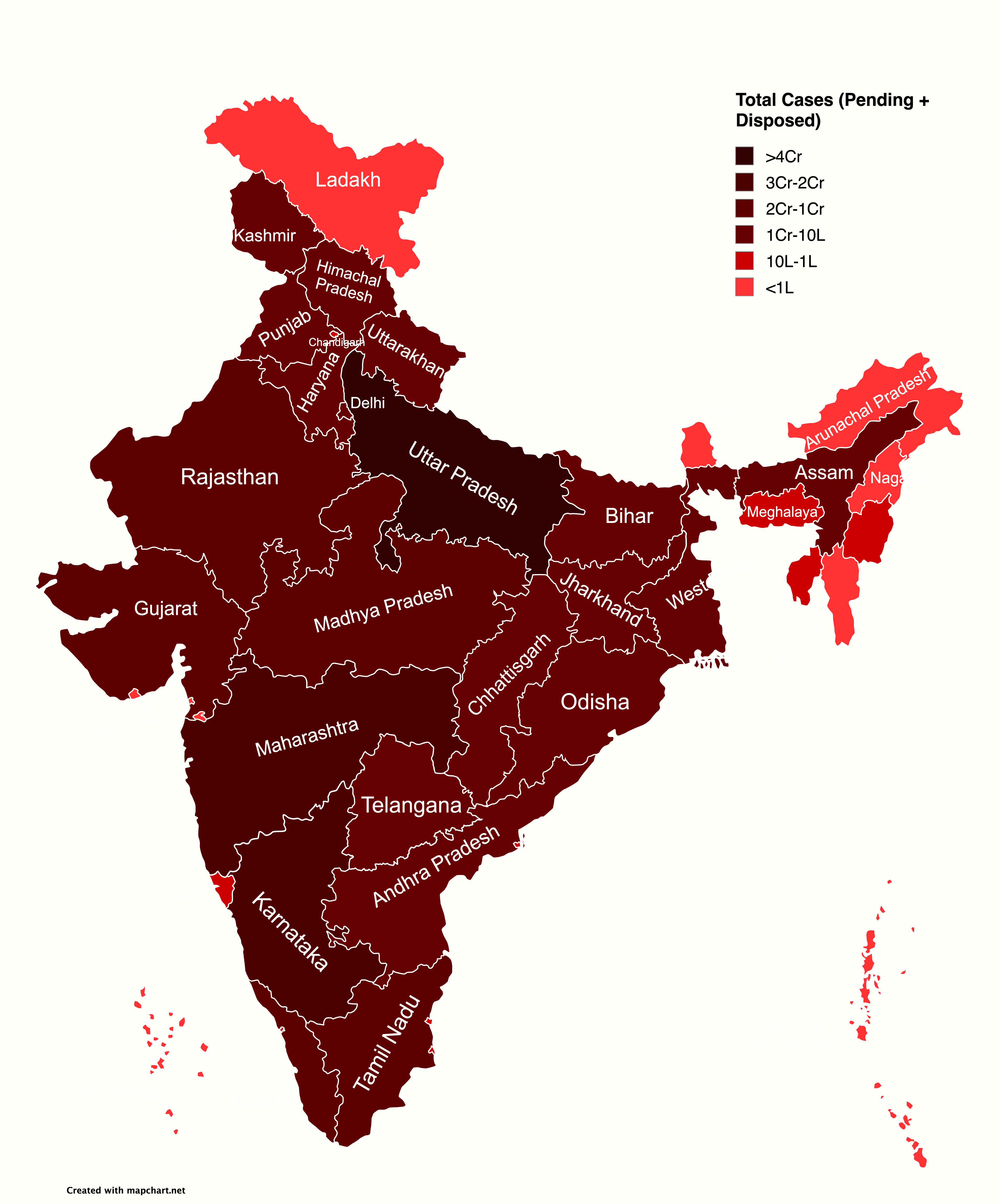
| S. no. | Court Name | Year Est. | Act Est. | Description | Updating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Supreme Court of India | 1950 | Constitution of India, 1950 | The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial authority in the country, with both original and appellate jurisdiction. It has the power to hear cases concerning fundamental rights, constitutional law, and national importance. It is the final court of appeal in all civil, criminal, and constitutional matters and plays a key role in upholding democracy, justice, and the Constitution. The Court has the authority to issue writs for the enforcement of fundamental rights under Article 32 and has the unique power to hear matters of national importance directly under its original jurisdiction. | Daily |
| Court Name | Year Est. | Act Est. | Description | Updating | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North | Allahabad High Court | 1866 | Indian High Courts Act, 1861 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| South | Andhra Pradesh High Court | 1954 | Andhra State Act, 1953 (re-established under Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014) | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| West | Bombay High Court | 1862 | Indian High Courts Act, 1861 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| East | Calcutta High Court | 1862 | Indian High Courts Act, 1861 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| Central | Chhattisgarh High Court | 2000 | Madhya Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2000 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North | Delhi High Court | 1966 | Delhi High Court Act, 1966 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North-East | Gauhati High Court | 1948 | Government of India Act, 1935 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| West | Gujarat High Court | 1960 | Bombay Reorganisation Act, 1960 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North | Himachal Pradesh High Court | 1971 | State of Himachal Pradesh Act, 1970 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North | Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh High Court | 1928 | Indian High Courts Act, 1861 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| East | Jharkhand High Court | 2000 | Bihar Reorganisation Act, 2000 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| South | Karnataka High Court | 1884 | Mysore High Court Act, 1884 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| South | Kerala High Court | 1956 | States Reorganisation Act, 1956 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| Central | Madhya Pradesh High Court | 1956 | States Reorganisation Act, 1956 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| South | Madras High Court | 1862 | Indian High Courts Act, 1861 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North-East | Manipur High Court | 2013 | North-Eastern Areas (Reorganisation) and Other Related Laws (Amendment) Act, 2012 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North-East | Meghalaya High Court | 2013 | North-Eastern Areas (Reorganisation) and Other Related Laws (Amendment) Act, 2012 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| East | Orissa High Court | 1948 | Orissa High Court Order, 1948 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| East | Patna High Court | 1916 | Indian High Courts Act, 1911 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North | Punjab and Haryana High Court | 1955 | Punjab Reorganisation Act, 1966 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| West | Rajasthan High Court | 1949 | Rajasthan High Court Ordinance, 1949 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North-East | Sikkim High Court | 1975 | Article 371F of the Constitution of India | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| South | Telangana High Court | 2014 | Andhra Pradesh Reorganisation Act, 2014 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North-East | Tripura High Court | 2013 | North-Eastern Areas (Reorganisation) and Other Related Laws (Amendment) Act, 2012 | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| North | Uttarakhand High Court | 2000 | Uttar Pradesh Reorganization Act, 2000, | Highest judicial authority at the state level, handling both original and appellate jurisdiction in civil and criminal matters. They supervise lower courts and tribunals within their territory and have the power to issue writs under Articles 226 and 227 of the Constitution. High Courts play a crucial role in upholding constitutional rights, resolving disputes, and ensuring the proper administration of justice in the state. | Daily |
| S. no. | Court Name | Year Est. | Act Est. | Description | Updating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | District Courts | Varies by District | Constitution of India, 1950, and State-specific Acts | District Courts in India are the principal courts of first instance for civil and criminal cases in each district. They handle a wide variety of cases, including family disputes, property issues, criminal matters, and civil suits. District Courts also deal with appeals from lower courts and tribunals within their jurisdiction. They play a significant role in the justice system by addressing cases at the grassroots level and ensuring the accessibility of justice for citizens in their respective districts. District Judges oversee these courts, ensuring fair trials and legal proceedings. | Daily |
| Court Name | Year Est. | Act Est. | Description | Updating | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADMINISTRATIVE AND SERVICE | Central Administrative Tribunal (CAT) | 1985 | Administrative Tribunals Act , 1985 | CAT addresses service-related grievances of central government employees, including those in All India Services, Union civil services, and certain public sector undertakings. Its jurisdiction covers matters like recruitment, promotions, transfers, and disciplinary actions. Designed for procedural efficiency, CAT allows aggrieved employees to represent themselves without legal counsel. It operates independently of conventional civil courts, providing a specialized forum for administrative disputes | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) | 1941 | Income-tax Act, 1922 | Final fact-finding authority for direct tax appeals under the Income Tax Act. Adjudicates disputes involving undisclosed income, fictitious transactions, cross-border remittances, and search & seizure assessments. Also hears matters where criminal prosecution under tax law is initiated, typically arising from findings of willful evasion or misreporting by the Assessing Officer. Jurisdiction extends to both individuals and corporate taxpayers, including HUFs and foreign entities | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Customs, Excise and Service Tax Appellate Tribunal (CESTAT) | 1982 | Customs Act, 1962 | Appellate body for disputes under indirect tax laws such as Customs Act, Central Excise Act.Hears appeals from tax commissioners involving issues like duty classification, tax valuation, refund denials, exemption eligibility, and anti-dumping duties. It serves both individuals and companies, with appeals on law going to the Supreme Court | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) | 2016 | Companies Act, 2013 | Adjudicates corporate disputes including insolvency proceedings, voluntary and compulsory liquidation, and corporate restructuring through schemes of amalgamation or demerger. Has exclusive jurisdiction over cases of shareholder oppression, mismanagement, and statutory breaches involving MoA/AoA. Also oversees matters under the Companies Act, IBC, LLP Act. | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) | 2016 | Companies Act, 2013 | National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) serves as the apex appellate authority for corporate legal matters in India. It hears appeals against orders passed by the National Company Law Tribunal. Additionally, NCLAT adjudicates appeals against decisions made by the Competition Commission of India (CCI) and the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA). Functioning as a quasi-judicial body, its decisions are binding and can be appealed to the Supreme Court of India on substantial questions of law. | Daily |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | National Green Tribunal (NGT) | 2010 | National Green Tribunal Act, 2010 | Original jurisdiction over disputes arising from environmental laws, including Environment Protection Act, Water Act, and Air Act. It deals with industrial pollution, illegal construction in eco-sensitive zones, forest clearance violations, and projects causing ecological harm. It can award compensation, pass injunctive relief, and enforce restoration of the environment, often against government bodies or industries | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT) | 1995 | Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 | An appellate forum under the SEBI Act, SARFAESI Act, and related laws, hearing appeals against regulatory orders by SEBI, IRDAI, and PFRDA. It covers insider trading, market manipulation, IPO misstatements, non-compliance with listing obligations, and penalties against intermediaries like stockbrokers, mutual funds, or listed companies | Daily |
| SECTORAL AND REGULATORY | Telecom Disputes Settlement and Appellate Tribunal (TDSAT) | 2000 | Telecom Regulatory Authority of India Act, 1997 | A specialized forum under the TRAI Act that adjudicates disputes in the telecom, broadcasting, and IT sectors. Jurisdiction includes issues such as license fee disputes, service quality complaints, interconnectivity problems, and tariff regulation. It hears cases from telecom operators, broadcasters, consumers, and regulatory bodies like TRAI | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Debt Recovery Tribunal (DRT) | 1993 | Recovery of Debts Due to Banks and Financial Institutions Act, 1993 | A statutory tribunal under the RDDBFI Act and SARFAESI Act that deals exclusively with recovery of debts exceeding ₹20 lakh by banks and financial institutions. Jurisdiction includes suits for loan defaults, enforcement of mortgages, personal guarantees, and attachment of secured assets. It has powers equivalent to a civil court and bypasses the delays of regular courts to expedite financial recovery | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Debt Recovery Appellate Tribunal (DRAT) | 1993 | Recovery of Debts Due to Banks and Financial Institutions Act, 1993 | DRAT hears appeals against the orders of Debt Recovery Tribunals (DRTs) in matters involving recovery of debts by banks and financial institutions. It adjudicates disputes relating to enforcement of security interests, borrower defaults, and actions under the SARFAESI Act. DRAT is the final appellate forum in the debt recovery hierarchy before constitutional courts. | Daily |
| ADMINISTRATIVE AND SERVICE | Armed Forces Tribunal (AFT) | 2009 | Armed Forces Tribunal Act, 2007 | A statutory tribunal under the Armed Forces Tribunal Act, 2007, established to adjudicate service-related matters of personnel from the Army, Navy, and Air Force. It hears appeals, complaints, and disputes concerning appointments, conditions of service, promotions, disciplinary actions, and court-martial verdicts. Composed of Judicial and Administrative Members, the tribunal has powers similar to a High Court and provides armed forces personnel a dedicated legal forum outside the chain of command | Daily |
| SECTORAL AND REGULATORY | Appellate Tribunal for Electricity (APTEL) | 2004 | Electricity Act, 2003 | Established under the Electricity Act, 2003, APTEL adjudicates appeals against orders from the Central and State Electricity Regulatory Commissions, Joint Commissions, and Adjudicating Officers. Its jurisdiction encompasses disputes related to electricity tariffs, licensing, grid operations, and regulatory compliance | Daily |
| SECTORAL AND REGULATORY | Railway Claims Tribunal (RCT) | 1989 | Railway Claims Tribunal Act, 1987 | RCT adjudicates claims against Indian Railways concerning compensation for loss, destruction, damage, deterioration, or non-delivery of goods and animals entrusted for carriage. It also addresses compensation claims relating to death or injury to passengers due to railway accidents. The RCT operates with powers equivalent to a civil court, and appeals against its decisions lie with the respective High Courts. | Daily |
| ADMINISTRATIVE AND SERVICE | Central Government Industrial Tribunal (CGIT) | 1965 | Industrial Disputes Act, 1947 | CGIT was set up under the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947, to settle industrial disputes involving employees of central government establishments and industries like banking, insurance, railways, and public sector units. It deals with issues such as wages, working hours, retrenchment, layoffs, and service conditions. The tribunal acts as a specialised forum to provide fair and timely resolutions between employers and workers, reducing the need for long court proceedings. | Daily |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC) | 1988 | Consumer Protection Act, 1986 | NCDRC is the apex consumer forum in India. It hears original complaints where the value of goods or services exceeds ₹10 crore, and also functions as the appellate authority for decisions passed by State Commissions. It adjudicates matters involving deficiency in service, defective products, unfair trade practices, and product liability claims against corporations, service providers, and e-commerce platforms | Daily |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (SCDRC) | 1988 | Consumer Protection Act, 1986 | SCDRC hears original complaints valued between ₹50 lakh and ₹10 crore, and appeals from District Forums within its territorial jurisdiction. It deals with consumer disputes involving housing, healthcare, banking, insurance, and retail sectors. The commission has powers to award compensation, refund, and direct corrective action against sellers or service providers | Daily |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | District Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (DCDRC) | 1988 | Consumer Protection Act, 1986 | DCDRC serves as the first tier of the consumer redressal mechanism. It has original jurisdiction to adjudicate complaints where the value of goods or services does not exceed ₹50 lakh. The commission hears disputes involving defective products, deficient services, and unfair trade practices across sectors like retail, travel, real estate, and personal finance. Here, complainants may appear without legal representation. | Daily |
| ADMINISTRATIVE AND SERVICE | State Administrative Tribunal (SAT) | 1985 | Administrative Tribunals Act , 1985 | SAT adjudicates service-related disputes of state government employees. Functioning as a quasi-judicial body, it addresses matters concerning recruitment, promotions, transfers, and disciplinary actions within the state's civil services. SATs operate independently of the regular judiciary, providing a specialized forum for expeditious resolution of service matters, thereby reducing the burden on conventional courts. | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Authority for Advance Rulings (AAR) | 2017 | Goods and Services Tax (GST) Act, 2017 | Authority for Advance Rulings (AAR) provides binding decisions to applicants on specified tax matters before they undertake transactions. Taxpayers can seek rulings on issues such as the classification of goods or services, applicability of notifications affecting tax rates, determination of time and value of supply, and eligibility for input tax credit. The AAR aims to ensure clarity and prevent future disputes by offering definitive interpretations of GST provisions | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Appellate Authority for Advance Ruling (AAAR) | 2017 | Goods and Services Tax (GST) Act, 2017 | Appellate Authority for Advance Ruling (AAAR) serves as the appellate body for decisions made by the Authority for Advance Ruling (AAR). Both applicants and jurisdictional officers can appeal to the AAAR if aggrieved by an AAR ruling. | Daily |
| SECTORAL AND REGULATORY | Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA) | 2017 | Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act 2016 | It oversees matters related to land acquisition, allotment of alternative plots, evacuee property management, and housing loan recovery. The department comprises several branches including a dedicated RERA branch, and has limited public interaction, mainly through its land and property-related cells. Public grievances are addressed via CPGRAM and PGMS systems. | Daily |
| SECTORAL AND REGULATORY | Real Estate Appellate Tribunal (REAT) | 2017 | Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 | Aims to regulate and promote a transparent, efficient, and accountable real estate sector. It ensures timely project completion, equitable agreements between promoters and buyers, and speedy resolution of disputes. REAT enforces legal provisions, strengthens grievance redressal mechanisms, and fosters investor confidence, especially in affordable housing. | Daily |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | Environmental Appellate Authority | 2010 | National Green Tribunal Act, 2010 | Original jurisdiction over disputes arising from environmental laws, including Environment Protection Act, Water Act, and Air Act. It deals with industrial pollution, illegal construction in eco-sensitive zones, forest clearance violations, and projects causing ecological harm. It can award compensation, pass injunctive relief, and enforce restoration of the environment, often against government bodies or industries | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Prevention of Money Laundering Appellate Tribunal/ Appelate Tribunal under SAFEMA | The Prevention of Money-laundering Act(PMLA), 2003 | This national tribunal adjudicates appeals against forfeiture and attachment of illegally acquired property under five Central Acts—SAFEMA, NDPS Act, PMLA, Benami Transactions Act, and FEMA. It hears cases involving smuggling, drug trafficking, money laundering, benami holdings, and foreign exchange violations. The tribunal consolidates appellate functions under these economic and criminal statutes and is headquartered in New Delhi. | Daily | |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | Competition Appellate Tribunal (COMPAT) | 2016 | The Competition Act, 2002 | National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) serves as the apex appellate authority for corporate legal matters in India. It hears appeals against orders passed by the National Company Law Tribunal. Additionally, NCLAT adjudicates appeals against decisions made by the Competition Commission of India (CCI) and the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA). Functioning as a quasi-judicial body, its decisions are binding and can be appealed to the Supreme Court of India on substantial questions of law. | Daily |
| SECTORAL AND REGULATORY | Cyber Appellate Tribunal (CyAT) | 2017 | Information Technology Act, 2000 | A specialized forum, now merged with TDSAT, under the TRAI Act that adjudicates disputes in the telecom, broadcasting, and IT sectors. Jurisdiction includes issues such as license fee disputes, service quality complaints, interconnectivity problems, and tariff regulation. It hears cases from telecom operators, broadcasters, consumers, and regulatory bodies like TRAI | Daily |
| ADMINISTRATIVE AND SERVICE | Labour Appellate Tribunal | 1950 | Industrial Disputes Act, 1947 | CGIT was set up under the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947, to settle industrial disputes involving employees of central government establishments and industries like banking, insurance, railways, and public sector units. It deals with issues such as wages, working hours, retrenchment, layoffs, and service conditions. The tribunal acts as a specialised forum to provide fair and timely resolutions between employers and workers, reducing the need for long court proceedings. | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | Insurance Appellate Tribunal | 2016 | Insurance Act, 1938 | An appellate forum under the SEBI Act, SARFAESI Act, and related laws, hearing appeals against regulatory orders by SEBI, IRDAI, and PFRDA. It covers insider trading, market manipulation, IPO misstatements, non-compliance with listing obligations, and penalties against intermediaries like stockbrokers, mutual funds, or listed companies | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Foreign Exchange Appellate Tribunal (FEMA)/ SAFEMA | Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999 | This national tribunal adjudicates appeals against forfeiture and attachment of illegally acquired property under five Central Acts—SAFEMA, NDPS Act, PMLA, Benami Transactions Act, and FEMA. It hears cases involving smuggling, drug trafficking, money laundering, benami holdings, and foreign exchange violations. The tribunal consolidates appellate functions under these economic and criminal statutes and is headquartered in New Delhi. | Daily | |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | Food Safety Appellate Tribunal | 2015 | The Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 | Hears appeals against decisions made by Adjudicating Officers under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006. It ensures fair adjudication in cases involving food safety violations. Each tribunal is headed by a qualified judge and functions within its designated state jurisdiction. | Daily |
| SECTORAL AND REGULATORY | Airports Economic Regulatory Authority Appellate Tribunal (AERAAT) | Airports Economic Regulatory Authority of India Act, 2008 | This national tribunal adjudicates appeals against forfeiture and attachment of illegally acquired property under five Central Acts—SAFEMA, NDPS Act, PMLA, Benami Transactions Act, and FEMA. It hears cases involving smuggling, drug trafficking, money laundering, benami holdings, and foreign exchange violations. The tribunal consolidates appellate functions under these economic and criminal statutes and is headquartered in New Delhi. | Daily | |
| SECTORAL AND REGULATORY | Inter-State Water Disputes Tribunal | The Inter-State River Water Disputes Act, 1956 | Adjudicates disputes between states over the sharing of inter-state river waters. Established under the Inter-State River Water Disputes Act, 1956, its role is to investigate, resolve, and give binding decisions when negotiations between states fail. Its verdicts hold the force of law and are not subject to Supreme Court jurisdiction. | Daily | |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | Foreigner Tribunals (Assam) | 2005 | The Foreigners Act, 1946 | Quasi-judicial bodies that adjudicate cases of people whose citizenship status is questioned, especially during the process of updating the National Register of Citizens (NRC). Their decisions can lead to deportation or detention if an individual is found to be an illegal foreigner. | Daily |
| SECTORAL AND REGULATORY | Electricity Regulatory Commission | 1998 | Electricity Act, 2003 | Regulates inter-State transmission and tariffs, licenses transmission and trading entities, adjudicates disputes among power generators and licensees, and ensures quality, continuity, and reliability of electricity supply. It also sets grid and trading standards, promotes transparency, and advises the government on electricity policy, competition, efficiency, and investment in the sector. | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | Intellectual Property Appellate Board (IPAB) | 1958 | The Copyright(Amendment)Act, 2012 | Adjudicated disputes related to copyright registration, assignment, licensing, and unpublished Indian works under the Copyright Act, 1957. It also dealt with miscellaneous matters concerning copyright law. The board served as a specialized forum for resolving complex intellectual property issues. | Daily |
| ADMINISTRATIVE AND SERVICE | Joint Administrative Tribunal (JAT) | Administrative Tribunals Act, 1985 | To adjudicate service matters of government employees belonging to Union Territories or where two or more states opt to have a common tribunal instead of separate State Administrative Tribunals (SATs). | Daily | |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | Competition Commission of India | 2003 | Competition Act, 2002 | Entrusted with preventing practices that adversely affect market competition, ensuring freedom of trade, and safeguarding consumer interests. It promotes fair competition by regulating anti-competitive conduct, overseeing mergers and acquisitions, and addressing abuse of dominance—thereby fostering open, transparent, and competitive markets across India. | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | SEBI/SAT/PFRDA/IRDAI | 2007 | Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 1999 , Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 2013 | An appellate forum under the SEBI Act, SARFAESI Act, and related laws, hearing appeals against regulatory orders by SEBI, IRDAI, and PFRDA. It covers insider trading, market manipulation, IPO misstatements, non-compliance with listing obligations, and penalties against intermediaries like stockbrokers, mutual funds, or listed companies | Daily |
| ADMINISTRATIVE AND SERVICE | Central Information Commission (CIC) | 2005 | Right to Information Act, 2005 | Adjudicates second appeals under the Right to Information Act, 2005, and addresses complaints related to denial or obstruction of information access. It has powers to direct disclosures, ensure proper record-keeping, impose penalties for non-compliance, and monitor the overall implementation of the RTI framework. Its decisions are final and binding on public authorities. | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Appellate Authority for Industrial and Financial Reconstruction (AAIFR) | 1987 | Sick Industrial Companies (Special Provisions) Act, 1985 | Appellate body to hear appeals against decisions of the Board for Industrial and Financial Reconstruction (BIFR). It ensured legal oversight in matters related to the revival or winding up of sick industrial companies. | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Customs Authority for Advance Rulings (CAAR) | Customs Act, 1962 | Provides advance rulings on customs-related questions such as classification of goods, valuation, applicability of duty exemption notifications, and determination of country of origin. Its primary function is to offer clarity and legal certainty to importers/exporters before transactions, reducing future litigation. | Daily | |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | Central Sales Tax Appellate Authority | 2006 | Central Sales Tax Act, 1956 | Adjudicates disputes related to inter-state sales under the Central Sales Tax Act, 1956. It ensures uniform interpretation of CST laws across states and resolves disagreements between state authorities and dealers. | Daily |
| TAXATION AND ECONOMIC | State Taxation Tribunal | State-specific legislation | Adjudicate disputes related to state taxes such as sales tax, VAT, entry tax, and other local levies. These tribunals serve as appellate forums for resolving disputes between taxpayers and the state tax authorities, ensuring fair application of tax laws at the state level. | Daily | |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) | 2016 | Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016 | Regulates insolvency professionals, agencies, and information utilities under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016. It oversees insolvency resolution and liquidation processes for individuals and corporate entities, ensuring transparency, efficiency, and timely outcomes. | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Commission (MRTP) | 1970 | Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 | Investigate and control monopolistic and restrictive trade practices in India. Its primary function was to promote and maintain competition in the market by preventing unfair trade practices that could harm consumer interests. | Daily |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | Revisionary Authority under MMDR Act | 1957 | Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957 | Responsibility to review and revise orders issued by State Governments concerning major minerals. It ensures that decisions align with the provisions of the MMDR Act and its rules, and can direct the State Government to amend or review decisions that are inconsistent with the law. | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) | 2018 | Companies Act, 2013 | Independent regulator overseeing the auditing profession and accounting standards in India. Its primary functions include recommending accounting and auditing policies, conducting investigations into professional misconduct, and imposing sanctions on auditors and audit firms. | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | National Anti-Profiteering Authority (NAA) | 2017 | Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST) Act, 2017. | Its primary function is to ensure that the benefits of tax reductions or input tax credits under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) regime are passed on to consumers by businesses, thereby preventing profiteering. | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | Copyright Board | 1958 | Copyright Act, 1957 | Resolved disputes related to copyright, such as licensing, assignment, and royalty rates. It had the authority to grant compulsory licenses and adjudicate issues concerning copyright societies and works withheld from the public. | Daily |
| COMMERCIAL AND BUSINESS | Trade Mark Registry (TMR) | 1940 | Trade Marks Act, 1999 | It operates under the administration of the Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trade Marks, functioning as the Registrar of Trade Marks. The TMR's primary role is to facilitate the registration of trademarks, ensuring they meet the necessary criteria and providing better protection against fraudulent use. | Daily |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | CCPA - Central Consumer Protection Authority | 2020 | Consumer Protection Act, 2019 | Regulate matters relating to violation of consumer rights, unfair trade practices, and false or misleading advertisements. It can order recall of unsafe goods, discontinue unfair practices, and impose penalties to safeguard consumer interests. | |
| CONSUMER, ENVIRONMENTAL AND OTHERS | News Broadcasting and Digital Standards Authority (NBDSA) | News Broadcasters and Digital Association (NBDA) | An independent self-regulatory body established by the News Broadcasters and Digital Association (NBDA), formerly known as the News Broadcasters Association (NBA). It was created to consider and adjudicate complaints about broadcasts |
| Regulators list | Update Frequency | Categorisation | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ace Derivatives & Commodity Stock Exchange Ltd (since closed) | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Association of Mutual Funds of India | Weekly | Industry Associations & Professional Bodies | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Banks – All orders | Weekly | Banking & Financial Sector Oversight | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Banks – Only wilful defaulters (CIBIL & Equifax) | Weekly | Banking & Financial Sector Oversight | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Board for Industrial & Financial Reconstruction (since dissolved) | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| BSE Ltd (including Arbitration Awards) | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Central Board of Indirect Taxes & Customs | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Handle investigations, prosecutions, and debt recovery) |
| Central Bureau of Investigation | Weekly | Enforcement & Recovery Bodies | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Central Depository Services (India) Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Company Law Board (since dissolved) | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Debt Recovery Tribunals | Weekly | Enforcement & Recovery Bodies | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Delhi Stock Exchange Ltd (since dissolved) | Weekly | Industry Associations & Professional Bodies | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Department of Income Tax | Weekly | Enforcement & Recovery Bodies | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation | Weekly | Enforcement & Recovery Bodies | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Indian Clearing Corp. Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Indian Commodity Exchange Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Insolvency & Bankruptcy Board of India - National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT, incl. NCLAT, HC & SC) | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Regulate securities, commodities, and market infrastructure) |
| Institute of Chartered Accountants of India | Weekly | Industry Associations & Professional Bodies | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Insurance Regulatory & Development Authority of India | Weekly | Industry Associations & Professional Bodies | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Inter-Connected Stock Exchange | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Metropolitan Stock Exchange of India Ltd (including Arbitration Awards) | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Adjudication Orders | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Easy Exit Scheme | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Official Liquidators | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Persons Disqualified from Directorship | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Registrars of Companies | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Serious Fraud Investigation Office | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Oversee corporate governance, insolvency, liquidation, disqualification, etc.) |
| Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Simplified Exit Scheme | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Banking regulation, financial crime monitoring, credit risk, housing finance, etc) |
| Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Vanishing Companies | Weekly | Corporate Affairs & Insolvency Authorities | (Banking regulation, financial crime monitoring, credit risk, housing finance, etc) |
| Ministry of Finance – Financial Intelligence Unit | Weekly | Banking & Financial Sector Oversight | (Banking regulation, financial crime monitoring, credit risk, housing finance, etc) |
| Ministry of Finance – Forward Markets Commission (since merged with SEBI) | Weekly | Banking & Financial Sector Oversight | (Banking regulation, financial crime monitoring, credit risk, housing finance, etc) |
| Multi Commodity Exchange Clearing Corp. Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Banking regulation, financial crime monitoring, credit risk, housing finance, etc) |
| Multi Commodity Exchange of India Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Banking regulation, financial crime monitoring, credit risk, housing finance, etc) |
| National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Handle investigations, prosecutions, and debt recovery) |
| National Commodity Clearing Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Handle investigations, prosecutions, and debt recovery) |
| National Financial Reporting Authority | Weekly | Industry Associations & Professional Bodies | (Handle investigations, prosecutions, and debt recovery) |
| National Housing Bank | Weekly | Banking & Financial Sector Oversight | (Handle investigations, prosecutions, and debt recovery) |
| National Securities Depository Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Handle investigations, prosecutions, and debt recovery) |
| National Spot Exchange Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Self-regulatory or professional organizations overseeing compliance within sectors) |
| National Stock Exchange of India Ltd (including Arbitration Awards) | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Self-regulatory or professional organizations overseeing compliance within sectors) |
| NSE Clearing Ltd | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Self-regulatory or professional organizations overseeing compliance within sectors) |
| Reserve Bank of India | Weekly | Banking & Financial Sector Oversight | (Self-regulatory or professional organizations overseeing compliance within sectors) |
| Securities and Exchange Board of India (including Consent Orders and actions, if any, taken by SAT) | Weekly | Financial Market Regulators & Exchanges | (Self-regulatory or professional organizations overseeing compliance within sectors) |
| United Nations Security Council | Weekly | Enforcement & Recovery Bodies | (Self-regulatory or professional organizations overseeing compliance within sectors) |
| Categorisation | State | From | Description | Update Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South | Andaman Nicobar | 2003 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| South | Andhra Pradesh | 2018 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North-East | Assam | 2020 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| East | Bihar | 2018 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| Central | CBI FIRs | 2016 | Corruption, bribery, financial scams, high-value frauds. | Monthly |
| North | Chandigarh | 2013 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| Central | Chhattisgarh | 2006 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| West | Dadra and Nagar Haveli | 2016 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| West | Daman and Diu | 2016 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North | Delhi | 2011 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North | Delhi Daily Arrest | 2021 | Similar to regular FIRs; includes bailable and non-bailable offenses. | Monthly |
| North | Delhi Motor Vehicle FIRs | 2015 | Property theft, encroachment, traffic accidents, license issues, etc. | Monthly |
| North | Delhi Property FIRs | 2016 | Property theft, encroachment, traffic accidents, license issues, etc. | Monthly |
| West | Goa | 2017 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| West | Gujarat | 2020 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North | Haryana | 2015 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North | Himachal Pradesh | 2016 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North | Jammu & Kashmir | 2020 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| East | Jharkhand | 2020 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| South | Karnataka | 2018 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| South | Kerala | 2014 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| South | Kerala Arrest | 2020 | Similar to regular FIRs; includes bailable and non-bailable offenses. | Monthly |
| Central | Madhya Pradesh | 2017 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| West | Maharashtra | 2019 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| West | Maharashtra Arrest | 2015 | Similar to regular FIRs; includes bailable and non-bailable offenses. | Monthly |
| North-East | Meghalaya | 2015 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| East | Odisha | 2017 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| South | Puducherry | 2016 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North | Punjab | 2015 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| West | Rajasthan | 2017 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North-East | Sikkim | 2014 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| South | Telangana | 2021 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North | Uttar Pradesh | 2017 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North | Uttarakhand | 2016 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| East | West Bengal | 2020 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North | Ladakh | 2018 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North-East | Manipur | 2019 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North-East | Arunachal Pradesh | 2015 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| North-East | Mizoram | 2020 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |
| South | Tamil Nadu | 2016 | Theft, assault, domestic violence, motor vehicle violations, cheating, cybercrime, NDPS cases, public order violations, etc | Monthly |